New Studies at ASCO 2022 Validate Effectiveness of Lunit AI as Diagnostic Aid in Cancer Treatment
30 May 2022 | Monday | News
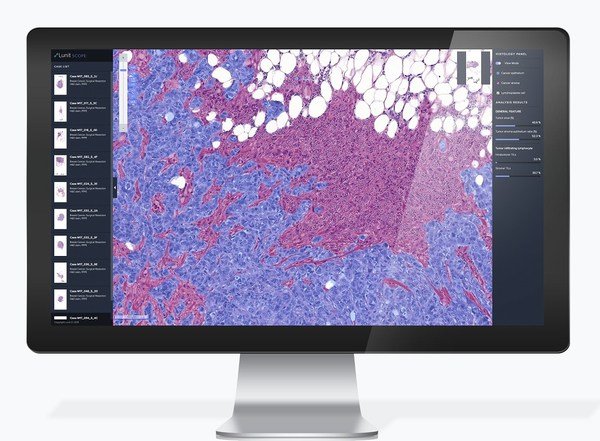
Lunit SCOPE IO
New findings demonstrate the clinical efficacy of AI-powered tissue analysis as a guide in cancer treatment, according to medical AI provider Lunit. The findings will be presented at the 2022 ASCO Annual Meeting, to be held from June 3 to 7. This year's ASCO meeting will showcase the largest number of studies by Lunit, including seven poster presentations and four online publications.
One of the poster presentations by Lunit elaborates on the validation of the Inflamed Immune Phenotype (IIP) as a practical biomarker to guide immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) treatment. The IIP is assessed by Lunit SCOPE IO, Lunit's AI-powered immune phenotype analyzer, from H&E slide images.
Lunit SCOPE IO analyzes a patient's cancer tissue slide image by observing the distribution of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes - TILs - one of the immunocytes that fight cancer cells. Based on the spatial distribution pattern of TILs and cancer cells in the tumor microenvironment, Lunit SCOPE IO identifies the tissue sample as one of three immune phenotypes: inflamed, immune-excluded, or immune-desert.
Findings upon evaluation showed that the Inflamed Immune Phenotype (IIP) may represent a practical, clinically actionable biomarker predictive of favorable ICI treatment outcomes across more than 16 primary cancer types. This study included more than 1,800 samples paired with real-world clinical outcomes data.
"Patient outcomes after ICI treatment were analyzed with specific indicators including objective response rate and progression-free survival. This study is especially noteworthy in that it demonstrates the utility of the AI-assessed IIP as a biomarker across diverse cancer patient populations, including those with PD-L1 negative, MSS/TMB-low tumors, in whom predictive biomarkers are urgently needed," said Chan-Young Ock, Chief Medical Officer at Lunit.
Lunit will also deliver a presentation on Lunit SCOPE PD-L1 TPS, the company's AI-powered PD-L1 tumor proportion score (TPS) analyzer.
"While PD-L1 expression is the standard biomarker for advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), manual evaluation of PD-L1 TPS by pathologists has practical limitations including interobserver variation and lengthy time demands," said Kyunghyun Paeng, Chief Product Officer of Lunit. "Through a randomized trial, this study aimed to test the benefit of our AI-based PD-L1 TPS analyzer in assisting pathologists' evaluation in terms of accuracy and evaluation time."
12 board-certified pathologists scored the PD-L1 TPS of 199 NSCLC whole-slide images in two separate intervals, with and without AI assistance, respectively. The results demonstrated the feasibility of Lunit SCOPE PD-L1 TPS to assist pathologists' evaluation: with AI assistance, the overall accuracy of pathologists' TPS scores increased from 79.9% to 83.2%, while the mean reading time was reduced by 30%.
Lunit SCOPE PD-L1 TPS recently received the CE mark, becoming the first Lunit SCOPE product to receive regulatory approval. Lunit is currently conducting a multi-center pivotal clinical trial in the U.S., following the results of this study.
The company's other scheduled poster presentations include a clinical trial demonstrating the accuracy of Lunit's AI imaging solution in detecting high-risk breast cancer patients, as well as a study assessing the clinical efficacy of Lunit SCOPE IO in the prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer patients.
"Lunit has been presenting groundbreaking findings at ASCO every year since 2019, and we are proud to showcase our largest set of research yet with 11 abstracts," said Brandon Suh, CEO of Lunit. "As our AI biomarker platform continues to gain validation and recognition, we are expanding our early research and commercial access programs for Lunit SCOPE throughout the year."
Most Read
- How Does GLP-1 Work?
- Innovations In Magnetic Resonance Imaging Introduced By United Imaging
- Management of Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma
- 2025 Drug Approvals, Decoded: What Every Biopharma Leader Needs to Know
- BioPharma Manufacturing Resilience: Lessons From Capacity Expansion and Supply Chain Resets from 2025
- APAC Biopharma Review 2025: Innovation, Investment, and Influence on the Global Stage
- Top 25 Biotech Innovations Redefining Health And Planet In 2025
- The New AI Gold Rush: Western Pharma’s Billion-Dollar Bet on Chinese Biotech
- Single-Use Systems Are Rewiring Biopharma Manufacturing
- The State of Biotech and Life Science Jobs in Asia Pacific – 2025
- Asia-Pacific Leads the Charge: Latest Global BioSupplier Technologies of 2025
- Invisible Threats, Visible Risks: How the Nitrosamine Crisis Reshaped Asia’s Pharmaceutical Quality Landscape
Bio Jobs
- Sanofi Turns The Page As Belén Garijo Steps In And Paul Hudson Steps Out
- Global Survey Reveals Nearly 40% of Employees Facing Fertility Challenges Consider Leaving Their Jobs
- BioMed X and AbbVie Begin Global Search for Bold Neuroscience Talent To Decode the Biology of Anhedonia
- Thermo Fisher Expands Bengaluru R&D Centre to Advance Antibody Innovation and Strengthen India’s Life Sciences Ecosystem
- Accord Plasma (Intas Group) Acquires Prothya Biosolutions to Expand Global Plasma Capabilities
- ACG Announces $200 Million Investment to Establish First U.S. Capsule Manufacturing Facility in Atlanta
- AstraZeneca Invests $4.5 Billion to Build Advanced Manufacturing Facility in Virginia, Expanding U.S. Medicine Production
News











