Leica Microsystems Launches Aivia 14 with Advanced AI for 3D Image Analysis
18 June 2024 | Tuesday | News
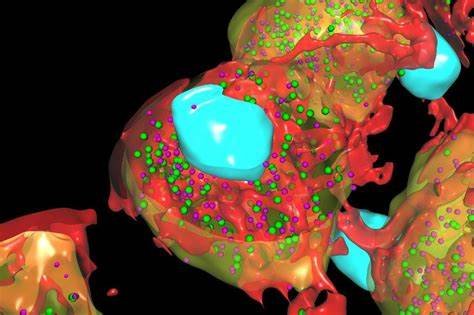
Image Source : Public Domain
Leica Microsystems, a leading provider of microscopy and scientific instrumentation, has released version 14 of Aivia, its flagship image analysis solution. This update introduces a suite of new features and enhancements for accurate deep-learning based cell segmentation, automated phenotyping and spatial data analysis in 3D multiplexed images. Researchers and scientists can visualize up to 15 channels in 3D multiplexed images simultaneously, providing a comprehensive view of complex biological processes.
“This major new version of Aivia is particularly well suited to contribute to drug development and will catalyze advances in cancer research, immunology and personalized medicine,” says Luciano Lucas, Director Data & Analysis at Leica Microsystems. “Aivia 14 enables users to systematically segment, phenotype and explore heterogeneities in healthy and pathological tissue microenvironments, and this will play a crucial role in determining treatment outcomes.”
"Dealing with massive numbers of data points in complex biological images can be daunting for researchers. Aivia 14 automates this process by leveraging advanced AI algorithms, allowing scientists to seamlessly identify and analyze phenotypes without the need to train deep learning models or code. This not only accelerates their research but also uncovers insights that might have otherwise been missed," adds Won Yung Choi, Product Manager, Data & Analysis at Leica Microsystems.
Aivia’s improved deep learning model accelerates cell detection by up to 78%, resulting in faster and more accurate detection and partition of cells. This enhancement enables characterization of tissue microenvironments and different phenotypes based on the expression of multiple biomarkers such as disease state or cell type. With the software’s updated dendrogram and dimensionality reduction tools, users can interactively explore phenotypes and gain a deeper understanding of 3D multiplexed image data.
Aivia 14 is available through flexible licensing models that provide users with options to meet their specific lab requirements
Most Read
- How Does GLP-1 Work?
- Innovations In Magnetic Resonance Imaging Introduced By United Imaging
- Management of Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma
- 2025 Drug Approvals, Decoded: What Every Biopharma Leader Needs to Know
- BioPharma Manufacturing Resilience: Lessons From Capacity Expansion and Supply Chain Resets from 2025
- APAC Biopharma Review 2025: Innovation, Investment, and Influence on the Global Stage
- Top 25 Biotech Innovations Redefining Health And Planet In 2025
- The New AI Gold Rush: Western Pharma’s Billion-Dollar Bet on Chinese Biotech
- Single-Use Systems Are Rewiring Biopharma Manufacturing
- The State of Biotech and Life Science Jobs in Asia Pacific – 2025
- Asia-Pacific Leads the Charge: Latest Global BioSupplier Technologies of 2025
- Invisible Threats, Visible Risks: How the Nitrosamine Crisis Reshaped Asia’s Pharmaceutical Quality Landscape
Bio Jobs
- Sanofi Turns The Page As Belén Garijo Steps In And Paul Hudson Steps Out
- Global Survey Reveals Nearly 40% of Employees Facing Fertility Challenges Consider Leaving Their Jobs
- BioMed X and AbbVie Begin Global Search for Bold Neuroscience Talent To Decode the Biology of Anhedonia
- Thermo Fisher Expands Bengaluru R&D Centre to Advance Antibody Innovation and Strengthen India’s Life Sciences Ecosystem
- Accord Plasma (Intas Group) Acquires Prothya Biosolutions to Expand Global Plasma Capabilities
- ACG Announces $200 Million Investment to Establish First U.S. Capsule Manufacturing Facility in Atlanta
- AstraZeneca Invests $4.5 Billion to Build Advanced Manufacturing Facility in Virginia, Expanding U.S. Medicine Production
News











